Interesting Facts About Mind-Blowing Mushrooms
Did you know that mushrooms are more closely related to animals than plants? These fascinating organisms have existed for about a billion years and play significant roles in ecosystems. Fungi form vast underground networks, connecting plants and facilitating nutrient exchange. Some species even glow in the dark or exhibit carnivorous behavior. Mushrooms offer potential medicinal benefits, from cognitive enhancement to treating depression. They're also being explored for sustainable construction and space habitation. The largest living organism on Earth is actually a honey fungus spanning 10 square kilometers. As you explore the world of mushrooms, you'll uncover even more mind-blowing facts about these remarkable fungi.
This post may contain affiliate links. If you make a purchase through these links, I may earn a commission at no additional cost to you. Additionally, portions of this post may be generated using artificial intelligence (AI) technology. While we strive for accuracy, please be aware that AI-generated content may not always be perfect and should be fact-checked when necessary.
The Spatula Scoops
- Fungi have existed for about 1 billion years, with an estimated 2.2 to 3.8 million species, most still unidentified.
- The largest living organism is a honey fungus covering 10 square kilometers in Oregon, aged 2,400-8,000 years.
- Some fungi exhibit carnivorous behavior, capturing and digesting prey like nematodes in nutrient-poor environments.
- Approximately 70 species of fungi are bioluminescent, glowing to attract insects for spore dispersal.
- Psilocybin mushrooms can induce profound emotional experiences and alter perception, with potential therapeutic benefits for mental health.
Fungal Kingdom's Ancient Origins

Countless fungi have inhabited Earth for an astonishing billion years, making them among the oldest living organisms on our planet. When you consider the vast array of mushrooms you see today, you're witnessing the result of a long and fascinating evolutionary journey. These ancient organisms have played a vital role in shaping our world's ecosystems, contributing to nutrient cycling and the development of terrestrial habitats.
The fungal kingdom's diversity is mind-boggling, with estimates ranging from 2.2 to 3.8 million species globally. Surprisingly, over 90% of these species remain unidentified by science, highlighting the vast potential for discovery in the world of fungi. This presents an exciting opportunity for researchers and mycologists to explore and document new species.
Interestingly, fungi, including mushrooms, are more genetically similar to animals than plants. This unique evolutionary path sets them apart in the tree of life. Their remarkable adaptability has allowed them to thrive in diverse environments, from lush forests to extreme conditions like outer space. As you observe mushrooms in your surroundings, remember that you're looking at the descendants of ancient, resilient organisms that have shaped our world for eons.
Mycelium: Nature's Internet
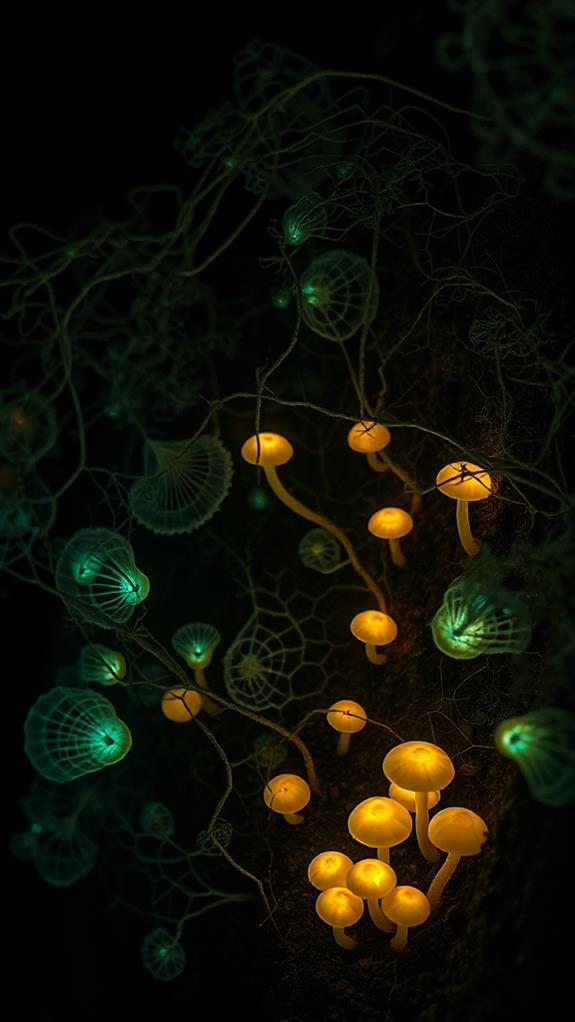
Hidden beneath the forest floor, an intricate network of fungal threads forms nature's own internet: mycelium. This underground web connects plants across vast distances, facilitating communication and resource sharing essential for ecosystem health. You might be surprised to learn that over 90% of plants rely on these mycorrhizal fungi for survival, accessing essential nutrients and water through their extensive networks.
Mycelium's reach is astonishing. Some networks, like the honey fungus in Oregon, span an impressive 10 square kilometers. These fungal threads act as nature's information superhighway, transmitting chemical signals that alert nearby plants to environmental stressors. This remarkable system enhances the resilience of entire ecosystems, helping plants withstand challenges like drought and disease.
The "Wood Wide Web," as it's often called, isn't limited to a single species. Mycelium can connect multiple plant types, fostering a complex web of interactions that contribute to overall forest health. By improving soil quality and plant robustness, these fungal networks play an essential role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting biodiversity in our natural world.
Bioluminescent Mushroom Species
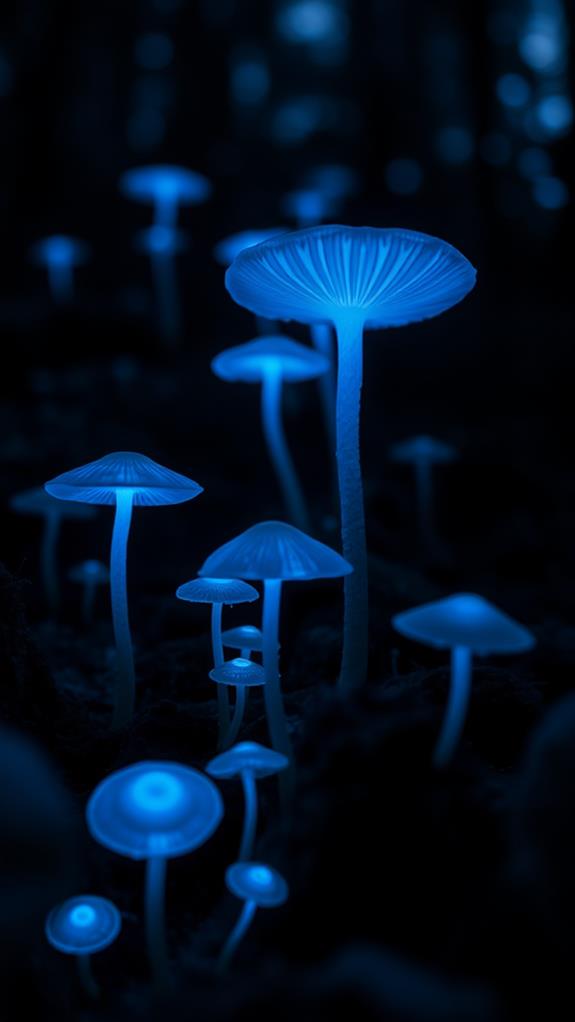

While mycelium operates in the unseen world beneath our feet, some mushrooms capture our attention with a mesmerizing glow. These bioluminescent fungi, numbering around 70 species, emit a natural light that's both fascinating and functional. You'll find this otherworldly glow primarily in damp, dark forests, where it creates an enchanting nighttime spectacle.
The secret behind this luminous display lies in a chemical reaction involving an enzyme called luciferase and a substrate known as luciferin. This process isn't just for show; it serves a vital ecological purpose. The light attracts insects, which then help disperse the mushroom's spores, aiding in reproduction.
If you're keen to spot these glowing wonders, look for species like the Jack-o'-lantern mushroom or the Ghost fungus. They're often found in moist forest environments, where their bioluminescence is most prominent. Remember, the darker and damper the conditions, the more likely you are to witness this magical phenomenon.
Understanding bioluminescent mushrooms offers insights into the complex world of fungi and their ecological roles. It's a reminder of nature's hidden marvels, waiting to be discovered in the depths of our forests.
Medicinal Properties of Fungi

Fungi's medicinal properties have captivated researchers and health enthusiasts alike. You'll find that certain mushrooms, like Lion's Mane and Cordyceps, are being studied for their cognitive-enhancing effects. Lion's Mane, in particular, stimulates nerve growth factor production, which can boost brain health and improve memory.
When it comes to mental health, magic mushrooms containing psilocybin have shown promise in treating depression and anxiety. Clinical studies have observed lasting mood improvements in participants after consuming these fungi.
Traditional medicine practices, such as Chinese medicine, have long revered fungi for their immune-boosting qualities and overall health benefits. The discovery of penicillin from Penicillium fungi revolutionized modern medicine, highlighting fungi's role in developing life-saving pharmaceuticals.
Here's a table summarizing some medicinal properties of fungi:
| Mushroom | Medicinal Property |
|---|---|
| Lion's Mane | Cognitive enhancement |
| Psilocybin | Depression and anxiety treatment |
| Cordyceps | Immune system support |
| Penicillium | Antibiotic production |
You'll also find that mushrooms contain various bioactive compounds that may help lower cholesterol, aid in cancer treatment, and support gut health. These properties demonstrate fungi's potential for holistic health benefits, making them a fascinating subject for ongoing research and medical applications.
Mushrooms in Space Exploration

You might be surprised to learn that mushrooms have a role in space exploration. Fungi's remarkable resistance to radiation makes them potential allies for protecting astronauts during long-duration missions. Scientists are even exploring the possibility of using mycelium, the root-like structure of fungi, to create living habitats on other planets, which could revolutionize how we approach space colonization.
Fungal Resistance to Radiation
Space-faring fungi might sound like science fiction, but certain mushroom species possess an extraordinary ability to withstand radiation levels that would be lethal to humans. You might be surprised to learn that fungi exist in environments where you'd least expect them, including space stations and highly radioactive areas.
Species like Cryptococcus neoformans and Aspergillus niger have shown remarkable resistance to radiation, surviving doses up to 1,000 times what would kill a human. These fungi have even thrived on the International Space Station, exposed to cosmic radiation for extended periods. Their resilience is attributed to unique biochemical properties, such as melanin production, which shields their cellular structures from radiation damage.
This radiation resistance isn't just a cool fact; it has practical applications. Scientists are studying these fungi to develop protective agents for space travel and long-duration missions beyond Earth. By understanding how these organisms withstand extreme conditions, we might reveal new possibilities for human space exploration. The potential biotechnological applications of these radiation-resistant fungi could revolutionize our approach to surviving in harsh environments, both on Earth and in space.
Mycelium-Based Space Habitats
While space exploration has long relied on metals and synthetic materials, scientists are now turning their attention to an unlikely source for building off-world habitats: mushrooms. Specifically, researchers are focused on mycelium, the root-like structure of fungi, for its potential in creating sustainable habitats on other planets and moons.
You might be surprised to learn that NASA has been exploring mycelium-based materials for constructing shelters on Mars. These organic compounds could potentially thrive in the planet's environment, offering a renewable resource for building structures. Mycelium's natural properties make it an excellent insulator and provide structural integrity, which are essential for protecting astronauts from harsh extraterrestrial conditions.
One of the most exciting aspects of mycelium-based habitats is their ability to absorb and convert carbon dioxide. This feature could play an important role in regulating atmospheric conditions within space colonies. Additionally, mycelium composites are being developed to be lightweight and durable, potentially replacing traditional construction materials for off-world settlements. These innovative materials could revolutionize how we approach space exploration and colonization, offering a sustainable solution for future astronauts.
Largest Living Organism on Earth

You might be surprised to learn that the largest living organism on Earth isn't a whale or a sequoia tree, but a honey fungus in Oregon. This massive fungal network, known as Armillaria ostoyae, covers an area of about 10 square kilometers and is estimated to be between 2,400 and 8,000 years old. It's not just big and old; this fungus plays an essential role in its ecosystem, breaking down dead wood and interacting with various plant species through its underground mycelium.
Honey Mushroom's Massive Network
Deep in Oregon's Blue Mountains lies an astonishing natural wonder: the world's largest living organism. This colossal entity isn't a towering tree or a sprawling coral reef, but a honey fungus known as Armillaria ostoyae. Spanning approximately 10 square kilometers, this massive network of interconnected mushrooms has captured the attention of scientists and nature enthusiasts alike.
You might be wondering how a fungus can achieve such an impressive size. The honey fungus spreads through an extensive underground mycelial network, connecting with other plants and fungi in the forest ecosystem. This network allows it to communicate and share resources across vast distances. As it grows, it feeds on both live and dead wood, playing a vital role in forest decomposition and nutrient cycling.
What's even more remarkable is the age of this fungal giant. Estimates suggest it's between 2,000 and 8,000 years old, making it one of the oldest living organisms on Earth. Its total biomass can weigh hundreds of tons, showcasing its significant ecological presence. This extraordinary organism demonstrates the incredible complexity and interconnectedness of forest ecosystems.
Age and Growth Span
When it comes to age and growth span, the honey fungus in Oregon's Blue Mountains stands unrivaled. This massive organism, scientifically known as Armillaria ostoyae, has been thriving for at least 2,400 years, with some estimates suggesting it could be up to 8,000 years old. You might be wondering how it's managed to survive for so long. The answer lies in its incredible adaptability and nutrient acquisition strategies.
| Characteristic | Detail | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 2,400-8,000 years | Demonstrates longevity |
| Size | 10 square kilometers | Largest known organism |
| Diet | Live and dead wood | Versatile nutrient source |
The honey fungus's extensive underground mycelial network allows it to spread and obtain nutrients efficiently. This network also facilitates communication with various plant species, contributing to the forest ecosystem's stability. As you explore the world of fungi, you'll find that the honey fungus exemplifies the resilience and ecological importance of these organisms. Its impressive age and growth span highlight the complex interplay between fungi and their environment, showcasing nature's ability to create truly mind-blowing organisms.
Ecological Impact and Resilience
The honey mushroom (Armillaria ostoyae) isn't just impressive for its age; it's also the largest known living organism on Earth. You'll find this massive honey fungus sprawling across approximately 10 square kilometers in Oregon's Blue Mountains. It's a reflection of nature's resilience, having survived for potentially over 8,000 years.
This colossal organism plays a vital role in forest ecosystems. As it feeds on both live and dead wood, the honey fungus contributes markedly to nutrient cycling. Its underground mycelium network connects with various organisms, showcasing the intricate web of forest life.
You might be surprised to learn that this single organism weighs hundreds of tons. It's a prime example of how much we still don't know about fungal biodiversity. Scientists have only identified about 6% of the estimated 3.8 million fungal species on Earth.
The honey fungus's remarkable size and longevity highlight its ecological impact and resilience. It's adapted to thrive in its environment, demonstrating nature's ability to create vast, interconnected systems that persist for millennia. This fungus serves as a reminder of the complex and often unseen relationships that shape our forests.
Carnivorous Mushroom Behavior

Mushrooms have turned the tables on their typical role as decomposers. You might be surprised to learn that some fungi, like the oyster mushroom, have developed carnivorous tendencies. These fascinating organisms have adapted to thrive in nutrient-poor environments by attracting and digesting tiny prey.
While they're not blue in color, these carnivorous mushrooms are certainly unique. They've evolved specialized structures to capture their meals efficiently. You'll find some with sticky surfaces or intricate traps designed to ensnare unsuspecting nematodes. Once caught, the mushroom releases enzymes that break down the prey's proteins, allowing it to absorb the nutrients directly.
This behavior showcases the incredible adaptability of fungi. By developing these carnivorous traits, they've found a way to supplement their diet when traditional decomposition isn't enough. It's an indication of the complexity of fungal life and raises intriguing questions about their ecological roles. As you explore the world of mushrooms, you'll discover that these organisms are far more than simple decomposers – they're resourceful survivors capable of surprising adaptations.
Fungi's Role in Ecosystem Health

Nature's unsung heroes, fungi play a vital role in maintaining ecosystem health. You might not see them, but these remarkable organisms are working tirelessly beneath your feet, decomposing organic matter and recycling nutrients back into the soil. This process is essential for supporting plant growth and sustaining the entire ecosystem.
Fungi's contributions to ecosystem health are multifaceted:
- They form symbiotic relationships with over 90% of terrestrial plants through mycorrhizal networks.
- They convert organic waste into nutrient-rich humus, improving soil fertility.
- They provide food and habitat for various wildlife, supporting biodiversity.
The fungus kingdom's impact on ecosystems is so significant that without them, many environments would face collapse. They're the linchpin in nutrient cycling, facilitating the transfer of essential elements between organisms and their surroundings. You'll find fungi acting as nature's recyclers, breaking down dead matter and making those nutrients available for new life. Their extensive underground networks, often called the "Wood Wide Web," allow plants to communicate and share resources, creating a complex and interconnected ecosystem that thrives on fungal activity.
Psychedelic Effects of Certain Mushrooms

You've likely heard about the psychedelic effects of certain mushrooms, particularly those containing psilocybin. These fungi can alter your consciousness, leading to profound experiences that some cultures have incorporated into spiritual rituals for centuries. Beyond their cultural significance, recent research has uncovered the therapeutic potential of these mushrooms, showing promise in treating mental health conditions like depression and anxiety.
Psilocybin's Effects on Consciousness
Consciousness altering substances have long fascinated humanity, and psilocybin stands out as one of nature's most intriguing psychedelic compounds. When you consume psilocybin, you'll experience profound changes in your perception, thought patterns, and emotional state. These effects typically last 4 to 6 hours, with intensity varying based on dosage and your mindset.
Psilocybin's impact on consciousness includes:
- Enhanced sensory perception
- Altered thought processes
- Profound emotional experiences
You might find yourself experiencing a sense of unity with nature or feeling transcendent during your trip. Many users report mystical experiences that can lead to lasting changes in their attitudes and behaviors. Curiously, psilocybin may also stimulate neurogenesis and the production of nerve growth factor, potentially improving your cognitive function and emotional well-being.
Research has shown promising results in using psilocybin to treat various mental health conditions. Clinical studies have explored its efficacy in addressing depression, anxiety, and PTSD, with some patients experiencing significant mood improvements after just one or a few sessions. As science continues to unravel psilocybin's effects on consciousness, we're gaining a deeper understanding of its potential therapeutic applications.
Therapeutic Potential of Psychedelics
Building on our understanding of psilocybin's effects on consciousness, let's explore the therapeutic potential of psychedelic mushrooms. Psilocybin mushrooms have shown remarkable promise in treating various mental health conditions. Clinical studies have demonstrated their effectiveness in alleviating depression, anxiety, and PTSD symptoms, with patients experiencing long-lasting mood improvements after just one or two sessions.
You might be wondering how these mushrooms work their magic. Research suggests that psilocybin stimulates the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein associated with neurogenesis and enhanced cognitive functions. This could explain why approximately 70% of participants report significant improvements in their mental health and overall well-being after psilocybin therapy.
The integration of psilocybin into psychotherapy, known as psychedelic-assisted therapy, is gaining traction for its ability to facilitate breakthroughs in treatment-resistant mental health issues. As a result, several jurisdictions have decriminalized or legalized psilocybin for therapeutic use, reflecting growing acceptance of its potential benefits. This shift in perspective could revolutionize mental health treatment, offering hope to those who've struggled with traditional therapies.
Cultural Significance and Rituals
Throughout history, certain mushrooms have held profound cultural significance due to their psychedelic properties. You'll find that these fungi, particularly psilocybin varieties, have been integral to spiritual and shamanic practices for thousands of years. Cultures worldwide have used them to facilitate deep spiritual experiences and gain insights into the nature of reality.
The cultural significance of psychedelic mushrooms is evident in various traditions:
- Siberian shamans consumed Amanita Muscaria to communicate with the spirit world
- Ancient Mesoamerican cultures incorporated psilocybin mushrooms into religious rituals
- Contemporary therapeutic practices draw inspiration from historical uses
You'll notice that these practices have sparked a renewed interest in the potential benefits of psychedelic mushrooms. Research has shown that psilocybin can lead to lasting mood changes and altered perceptions, reflecting its impact on consciousness and self-awareness. This historical and scientific background has fueled modern movements to legalize psilocybin for therapeutic uses.
As you explore this topic, you'll discover that the cultural significance of psychedelic mushrooms extends beyond ancient rituals, influencing contemporary discussions about mental health treatment and personal growth.
Do Ladybugs and Mushrooms Share Any Surprising Ecological Connections?
Ladybugs and mushrooms may not seem connected, but they both play vital roles in ecosystems. Ladybugs control aphid populations, while mushrooms break down organic matter to enrich soil. One of the interesting facts you never knew about ladybugs is that their survival indirectly benefits fungi by maintaining plant health in shared habitats.
Sustainable Materials From Mycelium

In light of growing environmental concerns, mycelium has emerged as a game-changing material for sustainable innovation. You'll be amazed at how this fungal network is revolutionizing various industries. Mycelium, the root-like structure of fungi, is being harnessed to create eco-friendly packaging materials that are both biodegradable and compostable. This offers a viable alternative to traditional plastics, reducing our reliance on harmful petrochemicals.
But that's not all. Companies are now developing mycelium-based textiles that can replace synthetic fabrics, further decreasing our dependence on fossil fuels. In the construction industry, mycelium composites are being used as building materials, providing natural insulation and temperature regulation. This contributes to improved energy efficiency in buildings.
What's more, cultivating mycelium is incredibly resource-efficient. It requires considerably less water and land compared to conventional farming practices. This makes it a more sustainable agricultural option. Additionally, researchers are exploring mycelium's potential in soil restoration and remediation. By harnessing the power of this fungal network, we may be able to improve soil health and restore ecosystems that have been degraded by human activity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Some Unique Facts About Mushrooms?
You'll be amazed by these fungal facts that'll mushroom your knowledge! Mushrooms belong to their own kingdom, with an estimated 3.8 million species worldwide. The honey fungus is the largest living organism, spanning 10 square kilometers. Fungi play an essential role in rainforest ecosystems, with 90% of raindrops originating from fungal spores. Golden oyster mushrooms can release 30,000 spores per second. Some fungi, like oyster mushrooms, are carnivorous, attracting and digesting nematodes.
What Are 5 Interesting Facts About Fungi?
You'll be amazed by these five fascinating fungi facts. First, there are an estimated 3.8 million fungal species, yet over 90% remain unexplored. Second, the honey fungus is the world's largest living organism, spanning 10 square kilometers. Third, fungi play an essential role in rainforest ecosystems, with 90% of tropical raindrops originating from fungal spores. Fourth, fungi use convective air flows and evaporative cooling for spore dispersal. Finally, the discovery of penicillin from mold revolutionized medicine, leading to numerous antibiotic developments.
What Is the Weird Brain Looking Mushroom?
You've stumbled upon a fascinating fungus! The weird brain-looking mushroom is *Gyromitra esculenta*, aptly nicknamed the "false morel." It's a peculiar sight with its brain-like, convoluted shape. While it might pique your curiosity, be cautious: this mushroom is highly toxic when raw. It contains gyromitrin, which can cause severe illness. Found in wooded areas during early spring, it's often mistaken for edible morels. Some cultures have preparation methods to reduce toxicity, but many experts still consider it unsafe.
What Are Some Fun Facts About Puffball Mushrooms?
You'll be fascinated by puffball mushrooms. They can release millions of spores in a single puff when mature and disturbed. You'll find them in various sizes, from marble-sized to soccer ball-sized. Some, like the giant puffball, are edible and nutrient-rich. You'll often spot them in fields, meadows, and forests, where they break down plant matter. As they age, their white interior turns into a dark, powdery mass. Remember, they're spherical and resemble balls or clouds.





